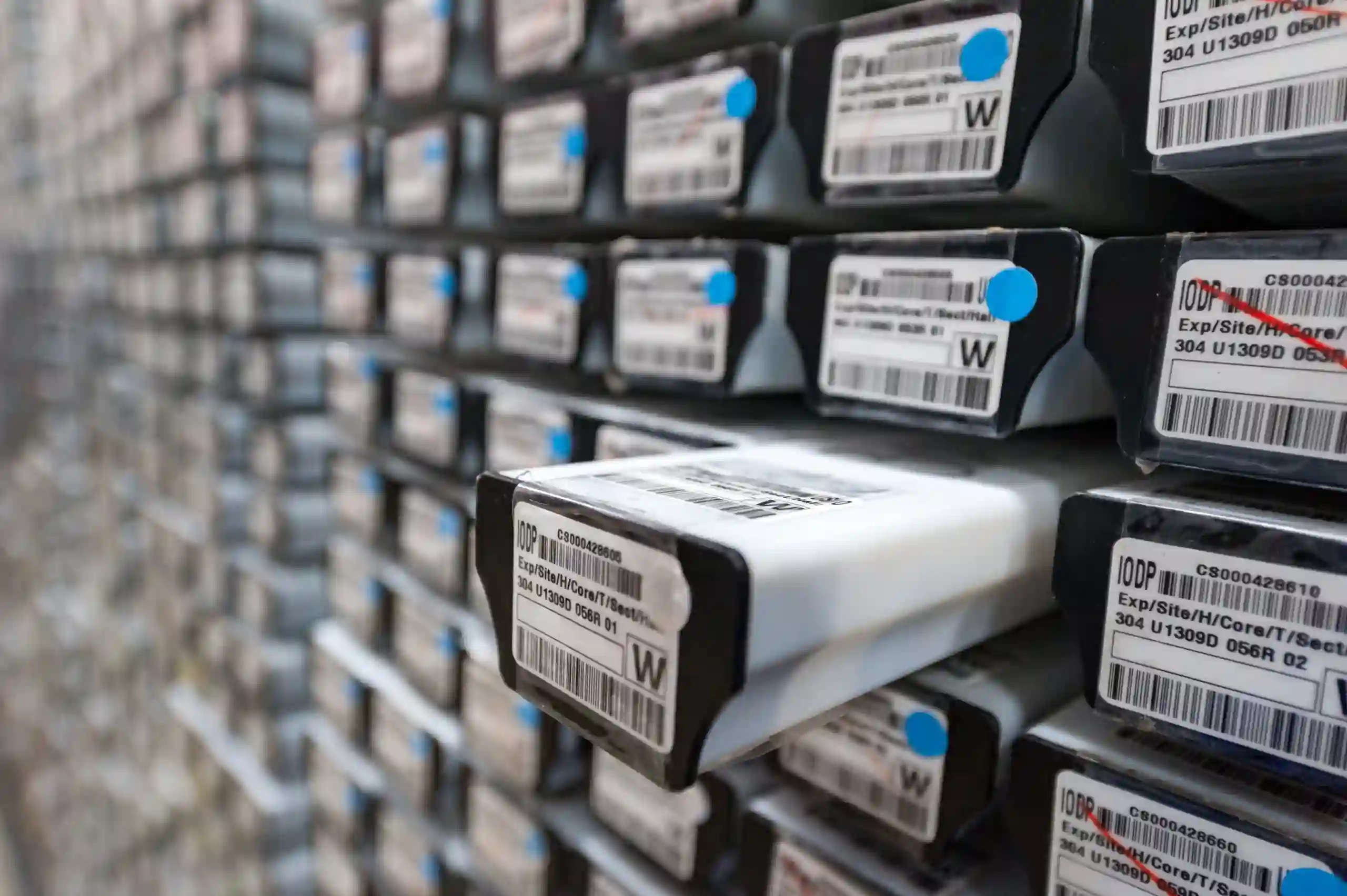
In a realm where precision dictates the rhythm of operations, the emergence of barcode scanning technologies has acted as a symphony conductor orchestrating a harmonious flow in inventory management.
The age of manual counting, prone to human error, has given way to an era of barcode brilliance, unfurling a tapestry of accuracy and efficiency across the warehouse landscape.
This evolution isn’t merely a tale of transitioning from analog to digital, but a narrative of how modern scanning technologies have entrenched themselves as the linchpin in contemporary inventory control.
Tracing the Origins: Barcode Technology’s Humble Beginnings
The genesis of barcode technology can be traced back to 1969, when Computer Identics unfurled a working barcode system, utilising laser beams to decipher information encapsulated in contrasting black and white bars. This nascent technology, albeit promising, grappled with the hurdles of standardization, which initially stifled its adoption. However, the dawn of the Universal Product Code (UPC) in 1973 marked a watershed moment, laying down the gauntlet for mainstream barcode adoption. The following year witnessed a Marsh supermarket in Ohio deploying a UPC-based barcoding system for the first time to log and sell a pack of Wrigley’s chewing gum, setting the stage for the barcode evolution.
- Key Milestones:
- 1969: Advent of the working barcode system by Computer Identics.
- 1973: Inception of the Universal Product Code (UPC), paving the path for standardized barcode technology.
- 1974: First-ever deployment of a UPC-based barcoding system in a Marsh supermarket1.
The Barcode Evolution: A Gateway to Modernised Inventory Management

As the veil of time unveiled, advancements in optics and computer technology catapulted barcode technology into a realm of enhanced efficacy. The symbiotic relationship between computing prowess and barcode technology burgeoned, unfurling a new era where automated inventory systems became the mainstay in inventory management. The upswing of computing power fanned the flames of barcode scanning adoption across a vast spectrum of industries, virtually banishing data entry inaccuracies to the annals of history.
The rippling effects of barcode scanning permeated through the veins of inventory control, mitigating the twin challenges of understocking and overstocking. This technological marvel not only curtailed data entry errors but also engendered the development of robust procurement strategies, ensuring a well-oiled supply chain. The capability to capture and process data at breakneck speed accentuated the real-time tracking of inventory, morphing erstwhile cumbersome processes into a seamless flow of operations.
- Impact Highlights:
- Error Reduction: Virtually eliminated data entry errors, a notorious challenge in manual inventory management.
- Optimized Stock Levels: Minimised the occurrences of understocking and overstocking through accurate data capture and processing.
- Procurement Planning: Facilitated the development of reliable procurement plans to meet demand efficaciously.
The narrative of barcode technology is akin to a riveting novel with many chapters, each delineating a significant evolution not only in scanning accuracy but also in how businesses manage their assets and inventory. The barcode, a seemingly simple array of black and white lines, has morphed into a powerful tool, rendering real-time inventory updates and automated order processing a reality. As we delve deeper, we will uncover how the torch of innovation is being carried forward by RFID technology, opening new vistas in inventory management and warehouse operational efficiency.
Here are some common barcode types used within warehousing.
| Barcode Type | Description |
|---|---|
| 1D (One Dimensional) Barcodes | |
| Code 39 | Alpha-numeric code widely used in various industries. Allows for 43 different characters. |
| Code 128 | High-density alpha-numeric code. Can encode all 128 ASCII characters and is more compact than Code 39. |
| UPC (Universal Product Code) | Used for retail items. Typically has 12 digits. |
| EAN (European Article Number) | Similar to UPC but has 13 digits. Used internationally. |
| Interleaved 2 of 5 | Numeric-only barcode used in warehousing and distribution. |
| Codabar | Older format often used in libraries and air cargo. |
| 2D (Two Dimensional) Barcodes | |
| QR Code (Quick Response) | Can store a lot of information in a small space. Often used for linking to websites or product information. |
| Data Matrix | Can store large amounts of data and is often used for labelling small items due to its compact size. |
| PDF417 | Can encode over 1,000 characters per symbol. Used for transport tickets, ID cards, and more. |
| Aztec | Often used in transportation settings for tickets, especially on mobile screens. |
RFID: The Next Frontier in Scanning Technology
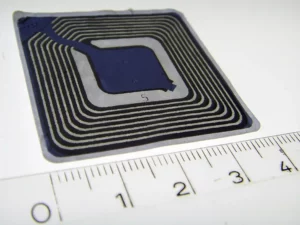
Emerging from the shadows of barcode technology, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) has heralded a new dawn in inventory management. Unlike its barcode counterpart that necessitates line-of-sight scanning, RFID technology facilitates the scanning of items en masse, significantly accelerating the inventory auditing process.
- Key Distinctions:
| Feature | Barcode Technology | RFID Technology |
| Line-of-sight | Required | Not Required |
| Scanning Speed | One at a time | Multiple at once |
| Range | Short (Few Centimetres) | Long (Up to few metres) |
| Data Storage | Limited | Extensive |
RFID tags, embedded with microchips, carry detailed information about the item they are affixed to, providing a treasure trove of data at the fingertips of inventory managers. This technology has not only boosted the speed of inventory auditing but has also elevated the accuracy level, providing real-time data about the location and status of assets1.
Bridging Physical and Digital Realms: Automated Inventory Systems
The advent of automated inventory systems has obliterated the chasm between the physical and digital realms of inventory management. By harnessing the power of barcode scanning, RFID tagging, and IoT sensors, these systems provide a continuous stream of real-time updates on stock levels, location, and movement of items.
- Core Components:
- Barcode Scanning: Enables precise identification and tracking of items.
- RFID Tagging: Facilitates mass scanning and real-time location tracking.
- IoT Sensors: Provide continuous monitoring and instant updates on environmental conditions and item status.
These technologies have converged to form a robust infrastructure, enabling real-time visibility, accurate tracking, and efficient handling of inventory. The integration of these technologies has not only streamlined inventory processes but has also spawned data-driven insights, empowering businesses to make informed decisions2.
Streamlining Warehouse Operations: The Barcode Impact
The ripple effects of barcode technology extend beyond the contours of inventory management into the broader landscape of warehouse operations. By assigning a unique identity to each rack, container, or item, barcode technology has significantly enhanced the efficiency of shipping, receiving, replenishing, picking, and packaging processes.
- Operational Enhancements:
- Shipping and Receiving: Accelerated processes and minimised errors.
- Replenishing: Ensured accurate stock levels and timely replenishment.
- Order Picking and Packaging: Enhanced accuracy and speed, reducing order fulfilment time.
The narrative of barcode technology and its profound impact on warehouse efficiency unveils a journey of continuous improvement. The ability to trace every item’s journey from the receiving dock to the shipping area has not only enhanced operational transparency but has also significantly curtailed errors, ensuring a smooth flow of operations.
The voyage of barcode technology from a nascent idea to a cornerstone of modern inventory management and warehouse operations epitomises the spirit of innovation. As we transition to the next segment, we will delve into the digital transformation heralded by mobile RF scanning and how warehouse automation is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in efficient warehousing and agile warehouse operations.
The Digital Transformation: From Paper to Mobile RF Scanning
The tapestry of warehouse management has seen a vibrant shift from paper-based processes to digital realms, with Mobile RF scanning spearheading this transformation. This shift is not merely a change in process; it represents an evolution towards agile warehouse operations and real-time data capture.
- Key Advancements:
- Instant Data Capture: Real-time capture and update of inventory data.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Significant reduction in data entry errors.
- Real-time Inventory Visibility: Instantaneous updates on inventory levels and location1.
Beyond Scanning: Exploring Warehouse Automation

The odyssey of scanning technologies doesn’t end at data capture; it extends into the realm of warehouse automation. The synergy between scanning technologies and automated systems has fostered a conducive environment for streamlined operations, reduced labour costs, and enhanced accuracy.
- Automation Components:
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): Enhance space utilisation and reduce retrieval time.
- Conveyor Systems: Facilitate seamless movement of goods within the warehouse.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Automates repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic roles.
The amalgamation of scanning technologies with automated systems has engendered a new era of efficient warehousing, turning erstwhile manual processes into a seamless orchestration of automated tasks.
Future Prospects: What Lies Ahead for Scanning Technologies?
The horizon of scanning technologies is expansive, with innovations like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and real-time tracking systems poised to further refine inventory management practices.
- Innovative Technologies:
- AI and ML: Predictive analysis for inventory forecasting and demand planning.
- Real-time Tracking Systems: Enhanced visibility and control over inventory and assets.
These future advancements promise to further enhance the real-time visibility and accuracy of inventory management, opening new vistas for operational efficiency and data-driven decision-making.
Lessons from the Field: Real-world Applications of Scanning Technologies
Unveiling real-world applications and case studies elucidates the transformative impact of modern scanning technologies on businesses and their inventory management processes. These real-world narratives offer a glimpse into the practical benefits and the challenges surmounted through the adoption of modern scanning technologies.
Making the Transition: How to Modernise Your Inventory Management
For businesses on the cusp of modernising their inventory management systems, embracing modern scanning technologies is a pragmatic step forward. This section provides a roadmap for making the transition, discussing the considerations, steps involved, and the myriad benefits awaiting.
- Transition Steps:
- Assessment: Evaluating the current inventory management system.
- Selection: Choosing the right scanning technology and automation systems.
- Implementation: Deploying the new system and training staff.
- Evaluation: Assessing the impact and making necessary adjustments.
Key Takeaways:
- Barcode and RFID technologies have revolutionised inventory management, ushering in a new era of accuracy, efficiency, and real-time visibility.
- The digital transformation from paper-based to mobile RF scanning has significantly enhanced data capture and inventory control.
- The integration of scanning technologies with automated systems has created a conducive environment for streamlined operations and reduced labour costs.
- Future advancements in scanning technologies promise to further refine inventory management practices, opening new vistas for operational efficiency and data-driven decision-making.
The quintessence of barcode brilliance lies in its ability to evolve, adapt, and continuously enhance the realm of inventory management. As we glimpse into the future, the potential for further advancements in scanning technologies beckons, promising to drive the narrative of inventory accuracy and warehouse efficiency to new heights.
Treading the Path of Evolved Inventory Management with PALLITE PIX
The narrative of modern scanning technologies unravelling the intricacies of inventory management is a testament to continuous innovation. As businesses strive to maintain a competitive edge, embracing the robustness of modern inventory systems becomes paramount. The journey doesn’t end at merely adopting barcode or RFID technologies; it extends to creating an ecosystem conducive for their optimal operation. This is where PALLITE’s PIX warehouse storage solutions come in.

PALLITE PIX is emblematic of how modern warehouse storage can be tailored to seamlessly integrate with the digital transformation witnessed in inventory management. Let’s delve into some compelling attributes of PALLITE PIX:
- Customisable: With the flexibility ranging from 4 to a whopping 400 pick-faces per unit, PALLITE PIX offers a scalable solution adapting to the evolving needs of your warehouse.
- Space-Saving: The ingenuity of design not only allows for the efficient utilisation of space but also paves the way for expansion as inventory levels burgeon. The modularity enables adding more units or reverting to a flat-packed state when not required, epitomising spatial efficiency1.
- Strong and Durable: Crafted with durable honeycomb paper cardboard walls and protected edges, these storage bins exhibit a remarkable load-bearing capacity of up to 500 Kg across each PIX storage unit, ensuring a long-lasting solution amidst the bustling activity of a warehouse.
The modular design of PALLITE PIX not only resonates with the ethos of flexibility but also aligns impeccably with modern barcode and RFID scanning technologies, fostering a harmonious interaction between physical storage and digital inventory management systems.
In the realm of ever-evolving warehouse operations, having a robust, flexible, and modern storage solution is not a luxury, it’s a necessity. The seamless fusion of PALLITE PIX with modern scanning technologies exemplifies a forward-thinking approach towards efficient warehouse management.
Elevate Your Warehouse Operations
Ready to transcend the conventional boundaries of warehouse management? Embrace the synergy of PALLITE PIX and modern scanning technologies to propel your inventory management into a realm of unmatched efficiency and accuracy.
Get in touch with PALLITE today, and explore how the PIX warehouse storage solutions can be the linchpin in revolutionising your warehouse operations, making them more agile, efficient, and responsive to the dynamic demands of the modern-day market.
Written by David Rose
